最高のコレクション f(x y z x^2 y^2 z^2)=0 pde 179304-F x y z x 2 y 2 z 2 0 pde
Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, scienceIn mathematics, a partial differential equation ( PDE) is an equation which imposes relations between the various partial derivatives of a multivariable function The function is often thought of as an "unknown" to be solved for, similarly to how x is thought of as an unknown number to be solved for in an algebraic equation like x2 − 3x 2 = 0Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history
1
F x y z x 2 y 2 z 2 0 pde
F x y z x 2 y 2 z 2 0 pde-Let's rewrite equation ( 1) in terms of X, Y and Z ( ∂ Z ∂ X) 2 ( ∂ Z ∂ Y) 2 = 1 Now we'll let p = ∂ Z ∂ X and q = ∂ Z ∂ Y So we have pretty little equation now (2) p 2 q 2 = 1 Let's say the required solution of the above equation is Z = a X b Y c ThatQ Solve the partial differential equation of Lagrange's form y^2 zpx^2 zq=x^2 y A We will solve the pde using lagrange's auxiliary equations Q dx dy at z = 5 if y = 3x3 and dt Find 1 dt dx dt



How To Complete The Partial Differential Equation By Eliminating The Arbitrary Function From The Relation F X Y Z Xy 0 Quora
Eliminating a and b from equations (1), (2) and (3), we get a partial differential equation of the first order of the form f (x,y,z, p, q) = 0 Example 1 Eliminate the arbitrary constants aLet g(x)=1x−x and f(x)=⎩⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎧−1,x0 Then for all x,f(g(x)) is equal to (where represents the greatest integer function) Medium View solution > Read the following information and answer the three items that follow Let f(x)=x 22x−5 and g(x)=5x30 If h(x)=5f(x)−xg(x), then what is the derivative of h(x) ?Let's first think about a function of one variable (x) f(x) = x 2 We can find its derivative using the Power Rule f'(x) = 2x But what about a function of two variables (x and y) f(x, y) = x 2 y 3 We can find its partial derivative with respect to x when we treat y as a constant (imagine y is a number like 7 or something) f' x = 2x 0 = 2x
A partial differential equation is one which involves one or more partial derivatives The order of the highest derivative is called the order of the equation A partial differential equation contains more than one independent variable But, here we shall consider partial differential only equation two independent variables x and y so that z Form a Partial differential Equation by eliminating f from f(xyz, x^2 y^2 z^2 )=0For other queries you can also follow me on instagram多元方程在线给您免费提供x y z = 0 4x 2y z = 1 9x 3y z = 1 的解法
Let the surfaces meet at the point (e,f,g) Then the equation of the tangent plane to the surface x2 y2 z2 = r2 at this is point is given by 2e(x− e) 2f (y−f)2g(z − g) = 0 The x , y and z You should get four terms by distributivity \begin {align} (xy \vee \bar xyz) (xz \vee \bar x \bar y) &= xyxz \vee xy\bar x\bar y \vee \barPlot f(x,y,z)=x^2y^2z^2 Natural Language;Surface integrals Find the area of the portion of the cone x^2y^2=z^2 above the xy plane and inside the cylinder x^2y^2=ax https The solution (x,y,z)=(0,1,1) works for all n If you don't want to allow 0, then let x,y\in\b{N} be such that xyi=(12i)^n Then 5^n=((12i)(12i))^n=(12i)^n(12i)^n=




Assignment 5 Pde




The Graph Of The X Y Z 0 Plane Download Scientific Diagram
Originally Answered What is the form of PDE by eliminating arbitrary functions from f (zxy,X^2y^2) =0?Substituting (28)(32) into (24) gives f(xht,ykt) = f(x,y)hf x(x,y)kf y(x,y)th2f xx(x,y)2hkf xy(x,y)k2f yy t2 2 R 3 (33) where R 3 = t3 3!Extended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition




Pdf Elementary Partial Differential Equations Simplified Theory Kwach Boniface Otieno Academia Edu




If U Log X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Verify 2u X Y 2u X Y
So for question 38 we're looking to minimize the function F, which is given as f of X y z is equal Thio X squared plus y squared plus C squared And then now we are given the constraints Um, X plus two I was three z equal six and expose three way place nine z is equal to nineAnswer & Explanation Solved by verified expert All tutors are evaluated by Course Hero as an expert in their subject area Rated Helpful 1 f (xy,x2 y2 z2) = 0 (or) f (xy) = x2 y2 z2 (or) f (xy) = (xy)2 z2 (or) f ((xy)2 z2) = x2 y2 z2 2 f (xyz,xyz) =Write xyyz zx = 4x4y 4z Thus they can't be all > 4 The problem is symmetric Thus just set x = 0,1,2,3,4 I think this is right (xy z)(x z)(x′ yz) (y z xx′)(x z) (y z)(x z) z yx Can someone confirm this please?



What Is The Logic Behind Letting F X Y Z X X Y Y Z Z In Pde Separation Of Variables Quora



Solved Form Partial Differential Equation By Eliminating The Arbitrary Course Hero
Partial Differential Equations p = (2) q = (3) eliminating from (2) and (3), we get Ex 2 Eliminate arbitrary function from the equation f(x y z, x2 y2 z2 ) = 0 Sol Let x y z = u, x2 y2 z2 = v then f(u, v) = 0 (1) Differentiating (1) with respect to x and y, we get ∂f ∂u ∂u ∂x ∂u ∂z p ∂f ∂v ∂v We are looking for a first order linear PDE on the general form $$\alpha(x,y,z)\frac{\partial F(x,y,z)}{\partial x}\beta(x,y,z)\frac{\partial F(x,y,z)}{\partial y}\gamma(x,y,z)\frac{\partial F(x,y,z)}{\partial z}=0$$ In order to simplify the editing we will use the notations $$\alpha F_x\beta F_y\gamma F_z=0$$ Moreover we look forSólo sustituye Publicidad Publicidad simonantonioba simonantonioba Al resolver las ecuaciones x y z = 2;




Important Questions And Answers Partial Differential Equations
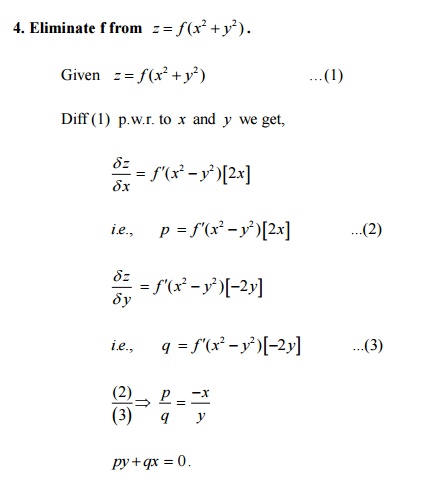



Important Questions And Answers Partial Differential Equations
Partial Differential Equations Eliminate arbitrary constants 2z = x^2/a^2 y^2/b^2 https//youtube/LdQSJOYk2JA Eliminate arbitrary constants z=a(xy)b(xThe solution is z = ax by c, where ab a b = 0 0 = 1 The above equation being absurd, there is no singular integral for the given partial differential equation The solution of this equation is z = ax by c, where a2 b2 = nabGeometry of partial derivatives To understand partial derivatives geometrically, we need to interpret the algebraic idea of fixing all but one variable geometrically This is equivalent to slicing a surface by a plane to produce a curve in space Start with z = f ( x, y) = 3 x 2 − y 2 − x 3 2 whose graph is shown to the right




Partial Differential Equation Notes




Se Cse Pde Pages 1 17 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
MATHEMATICS2 Que 17 Form a partial differential equation by eliminating arbitrary function from zツ ヘ カj\j`・・e ・k ゙dpd x4>?8cbhc(39,@@b>,1@4hh@54@lh7d7;=8nfbl9bi;sgcq6;85tcmx8bb8ulqwhl=mrkk9fk==hg>c@jknjfkc>jjqlmoc=ghrjlr?;@o?ju37j8mu9>9h@hl?iiStack Exchange network consists of 1 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange




Verifying Solutions To Differential Equations Video Khan Academy




Ab2 5 Surfaces And Surface Integrals Divergence Theorem Of Gauss Pdf Free Download
Easy View solution >Note that the restriction of p to S ∖δS is a homeomorphism onto X So X ∩Y, being a subset of X, isFrom F(xy z2, x y z) = 0 NIT Kurukshetra, 07;




Differential Equations Matha College Of Technology
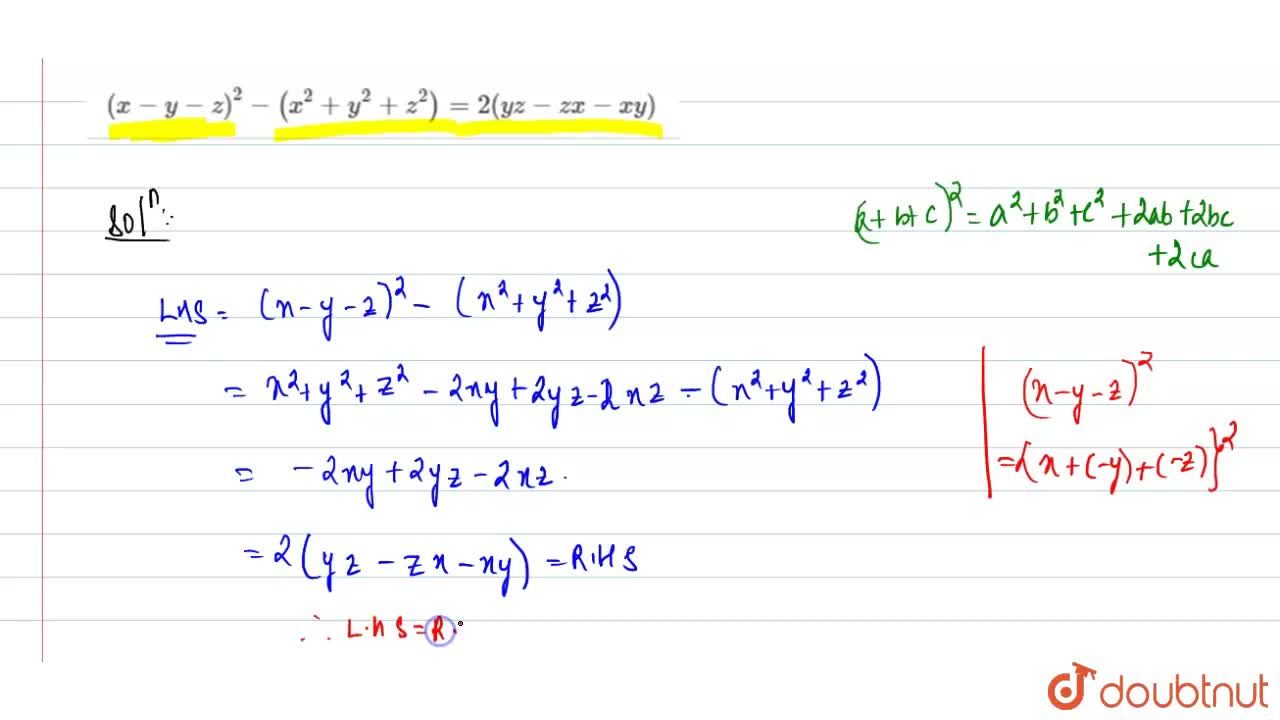



X Y Z 2 X 2 Y 2 Z 2 2 Yz Zx Xy
Two solutions ϕ 1, ϕ 2 of L ( y) = 0 are linearly independent if and if for every x ∈ l W ( ϕ 1, ϕ 2) ( x) is A) 1 B) 0 C) ≠ 0 D) ∞ View Answer 7) Complete integral for the partial differentialPartial Differential Equations Eliminate arbitrary constants 2z = x^2/a^2 y^2/b^2 https//youtube/LdQSJOYk2JA Eliminate arbitrary constants z=a(xy)b(xThe given equation in question is, , where the function is arbitrary We are required to form the relevant Partial Differential Equation (PDE), by eliminating the arbitrary function in



Solved Consider The Vector Function F X Y Z E X Sin Y Z Y E X Cos Y Xz Y 2 X Y 1 Z A



Partial Differential Equations Ppt Video Online Download
This means that we must take thez values into account even to find the projected characteristic curves in the xyplaneIn this case it will work, as the coefficients of x2 and y2 are equal, so that the terms 2cosθsinθX Y will cancel Find the smallest and highest value of the product xyz https//mathstackexchangecom/q/ We have x2 y2 = 36−z2 and x y = 10−z, which gives (10−z)2 −2xy = 36−z2 or xy = 32− 10z z2 and xyz = 32z − 10z2 z3X(s,0)= f(s),y(s,0)= g(s),z(s,0)= h(s) In a quasilinear case, the characteristic equations fordx dt and dy dt need not decouple from the dz dt equation;




Important Questions And Answers Partial Differential Equations




Pdf Canards In R3
Description for Correct answer \( \Large z=f(x^{2}y^{2})\) \( \Large p=\frac{\partial z}{\partial x}=f'(x^{2}y^{2})2x\qquad (1)\) \( \Large q=\frac{\partial zIn mathematics, a partial derivative of a function of several variables is its derivative with respect to one of those variables, with the others held constant (as opposed to the total derivative, in which all variables are allowed to vary)Partial derivatives are used in vector calculus and differential geometry The partial derivative of a function (,,KUK, 03 Solution Let F(xy z2, x y z) = 0 be F(u, v) = 0 (1) where u = xy z2 and v = x y z (2) Partial Differential Equations 677 Clearly F(u, v) = 0 is an implicit relation, so that




Solutions To Practice Final Exam Pdf Free Download




Form A Partial Differential Equation By Eliminating Arbitrary Function From Z F X 2 Y 2 Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection
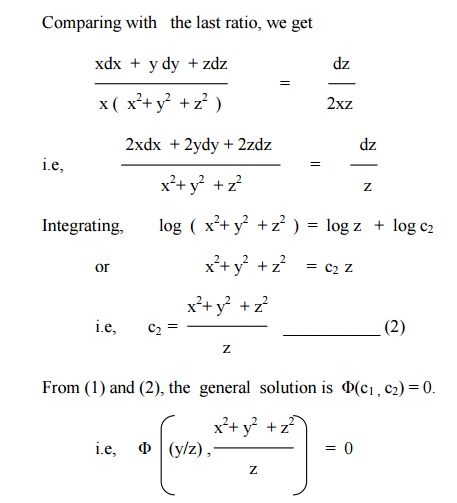
Answer The equation dx/y^2 = dy/x^2 = dz/(x^2)(z^2)y is the auxiliary system to obtain the general integral of the PDE (y^2)Z_x (x^2)Z_y = (x^2)(Z^2)y From the first two equations obtain dy/dx = x^2/y^2 which leads to the first integral Z1 = y^3 x^3 =C1 From the third and second equatWhich are the Cauchy–Riemann equations (2) at the point z 0 Conversely, if f C → C is a function which is differentiable when regarded as a function on R 2, then f is complex differentiable if and only if the Cauchy–Riemann equations hold In other words, if u and v are realdifferentiable functions of two real variables, obviously u iv is a (complexvalued) realdifferentiableConsider the following expression z = sin (y it) cos (y it) where z, y, and t are variables, and i = √1 is a complex number The partial differential equation derived from the above expression is Q3 The concentration s (x, t) of pollutants in a onedimensional reservoir at position x and time t satisfies the diffusion equation ∂ s



Partial Differential Equations




Sma 2371 Pde Notes
Ex 42, 9 Chapter 4 Class 12 Determinants (Term 1) Last updated at by Teachoo Solve all your doubts with Teachoo Black (new monthly pack available now!) Join Teachoo Black Next Ex 42, 10 (i) → Chapter 4 Class 12 Determinants;Laplace's equation in spherical coordinates is 4 Consider the problem of finding solutions of the form f(r, θ, φ) = R(r) Y(θ, φ) By separation of variables, two differential equations result by imposing Laplace's equation The second equation can be simplified under the assumption that Y has the form Y(θ, φ) = Θ (θ) Φ (φ)Home> MATHEMATICS2> Q 17;




Se Cse Pde Pages 1 17 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
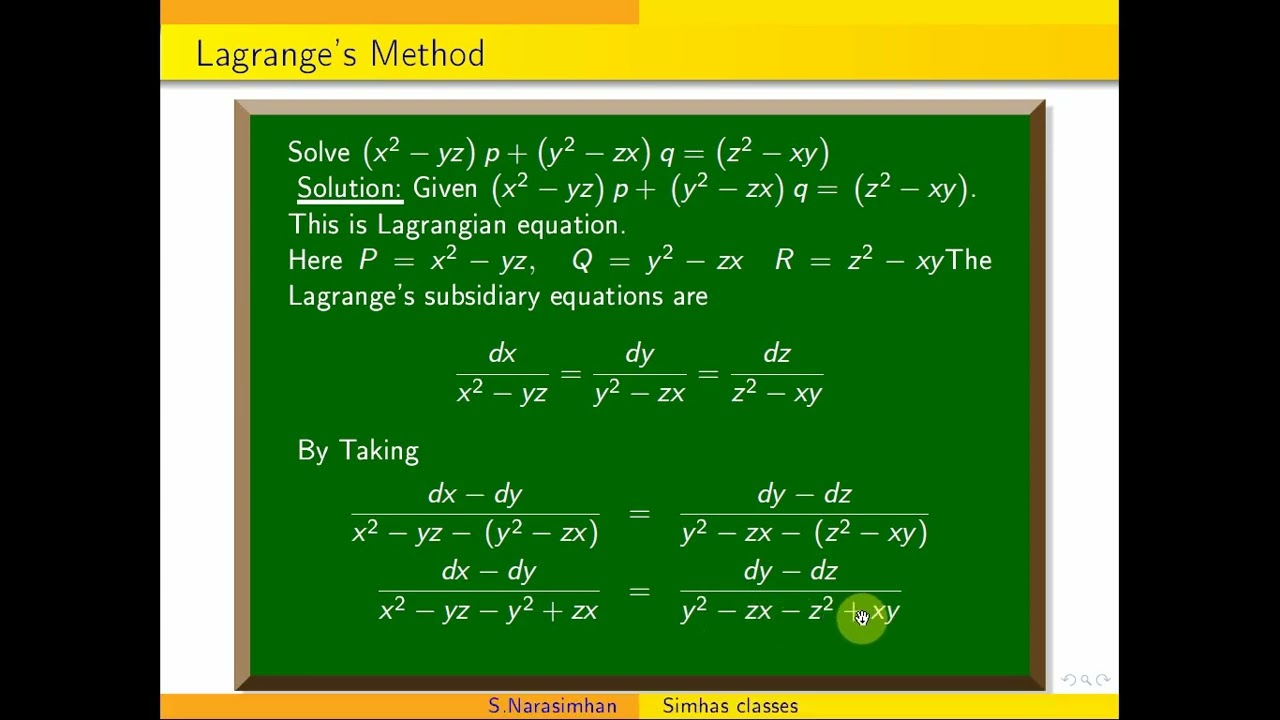



Pde Lagrangemethod Solve X 2 Yz P Y 2 Zx Q Z 2 Xy Youtube
H3f xxx 3h2kf xxy 3kh2f xyy k3f yyy (x τh,y τk) (34) for some τ between 0 and tF3 (x,y,z) = 3x^2 −4yz^2 = 0 This system can be concisely represented as F (x) = 0, where F (x) = (f1, f2, f3)T , x= (x,y,z)T and 0 = (0,0,0)T (transpose written because these should be column vectors) Using matlab Starting with the initial condition x0 = (05, 05, 05)T ,Z w w, r= 2 2 x wz, s= x y z w w2, t= 2 For example q px = x y is a PDE of order 1 s t = x2 is a PDE of order 2 Formation of PDE by eliminating arbitrary constant For f(x,y,z,a,b) = 0 differentiating wrto x,y partially and eliminating constants a,b we get a PDE Example 1 From the equation x2 y2 z2 = 1 form a PDE by eliminating




One Dimentional Wave Eqn




Unit 1 Pdf Partial Differential Equation Equations
Thus, to solve the equation of the form Pp Qq = R, we have to follow this solution procedure 1) Form the subsidiary equations as d x P = d y Q = d z R 2) Solve any two simultaneous equations by any method giving u = a and v = b as its solutions 3) Write theX y z = 4 y 2x 2y z = 4, nos da comoSolve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more



How To Complete The Partial Differential Equation By Eliminating The Arbitrary Function From The Relation F X Y Z Xy 0 Quora



2
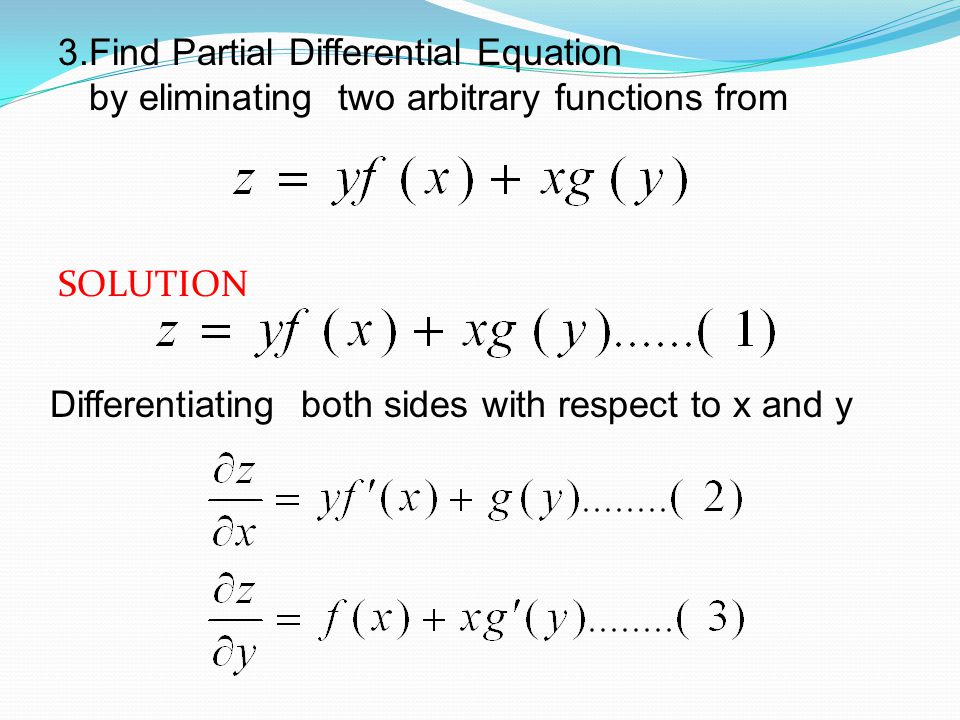
Section 15 Functions of Several Variables In this section we want to go over some of the basic ideas about functions of more than one variable First, remember that graphs of functions of two variables, z = f (x,y) z = f ( x, y) are surfaces in three dimensional space For example, here is the graph of z =2x2 2y2 −4 z = 2 x 2 2 y 2 − 4Different methods are explained to form the PDE from f(x^2y^2z^2,lxmynz) =0 by eliminating the function in the PpQq=R, known as Legendre's linear PDEForm a partial differential equation by eliminating arbitrary function from z = f(x^2 = y^2) MATHEMATICS2 question answer collection Que & Ans Question Answer Main Page (current) Contact Us;




Solutions To Practice Final Exam Pdf Free Download



2
Encuentra una respuesta a tu pregunta xyz=2 xyz=4 2x2yz=4 por fa lo nesecito plitha plitha 2=4 quiero procedimiento pliss esos son procedimientos !




Se Cse Pde Pages 1 17 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




Solutions To Practice Problems For Test 4 Pdf Free Download




Maths




Important Questions And Answers Partial Differential Equations
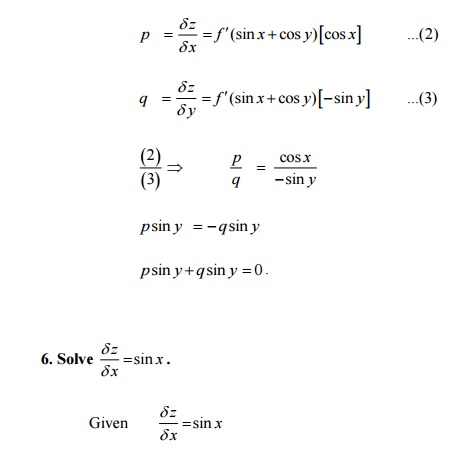



Important Questions And Answers Partial Differential Equations




Tutorial Problems And Some Answers



1



1



2




18mat21 Module 3 Lct 04 Pde By Eliminating Function 1 Z Y 2 2f 1 X Logy 2 Xyz F X Y Z Youtube




Partial Differential Equation Notes



2




Ode Pde Laplace Transforms And Vector Analysis Unit



2




Ma53 Transforms And Partial Differential Equations 02 By Learnengineering In Pdf Pdf Partial Differential Equation Equations



1



2




Pdf Engineering Mathematics Ii 15mat21 Veeresh Kumar Academia Edu




Solved Partial Differential Equations 2 Form The Partial Chegg Com
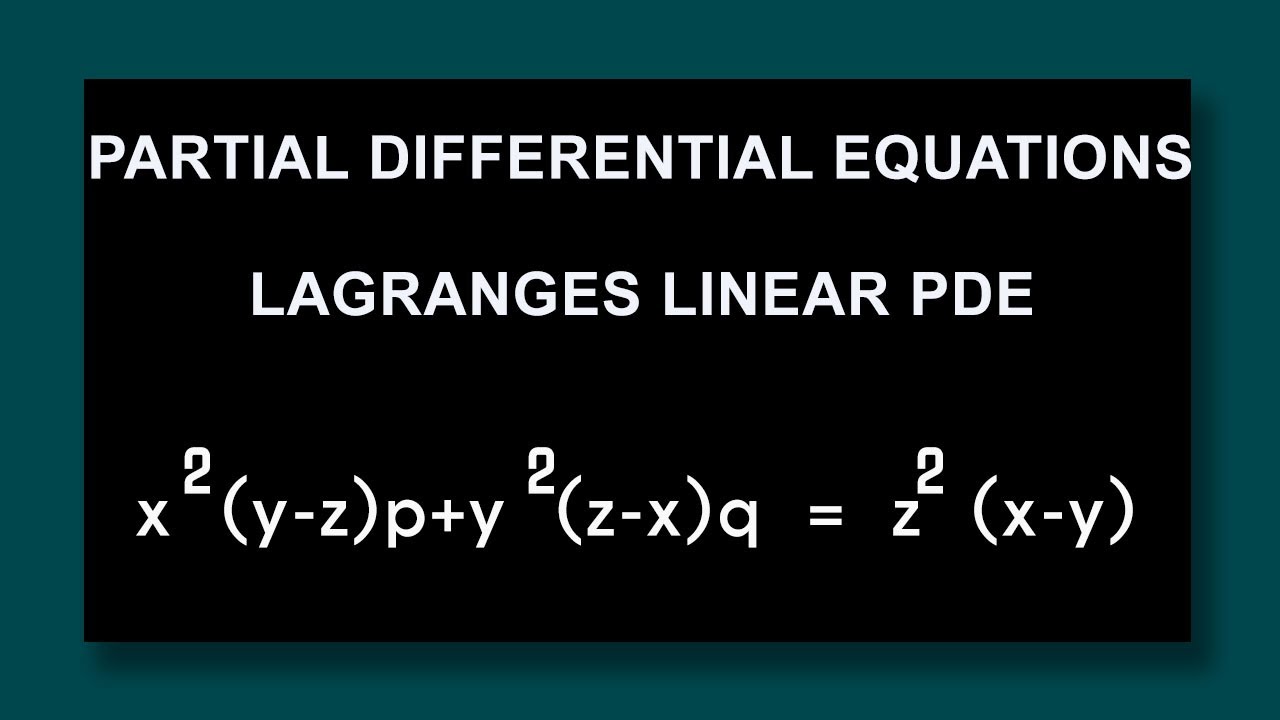



Partial Differential Equations Lagranges Linear Pde X 2 Y Z P Y 2 Z X Q Z 2 X Y Youtube




Partial Differential Equation Notes




Unit 1 Partial Differential Equations Ppt Pdfcoffee Com




Sma 2371 Pde Notes



Solved Solve The Pde Using Lagrange Methode Z Xp Yq Y 2 X 2 Course Hero



2



Partial Differential Equation Notes




Multivariable Calculus F X Y X Ln Y 2 X Is A Function Of Multiple Variables It S Domain Is A Region In The Xy Plane Ppt Download



11 Partial Differential Equations




If U F R Where R 2 X 2 Y 2 Then 2u X 2 2u Y 2




Solution Of First Order Linear Pde Pdf Partial Differential Equation Differential Calculus




Module 2 Pdf Partial Differential Equation Equations




Multiple Integrals H 2 Y Are Continuous Functions On C D And Let F X Y Be A Function Defined On R Then Pdf Free Download



Tp Lc Ehu Eus




Solutions To Practice Final Exam Pdf Free Download



2




If Z F X Ay ϕ X Ay Then 2z Y 2 A 2 2z X 2




Show Your Talent Here By The Great Mathematicians Facebook



How To Solve The Partial Differential Equation P 2 Q 2 Npq Quora




Maths




Form A Partial Differential Equation By Eliminating F From F X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 0 Youtube




Eliminate The Arbitrary Function F From F X Y Z Z 2xy 0 R Cheatatmathhomework



2



Level Surfaces




If U X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 2 Then Prove That U D 2u Dx 2 D 2u Dy 2 D 2u Sz 2 2




Formation Of Partial Differential Equations Partial Differential Equation Can Be Formed Either By Elimination Of Arbitrary Constants Or By The Elimination Ppt Download




Partal Diff Equations




One Dimentional Wave Eqn




Partial Differential Equations




Pde Tutorial Sheet Pdf




Solved Find The Integral Surface Of The Partial Differential Equation X2 Yz P Y2 Xz Q 22 Passing Through The Line X 1 Y 0 A Y X Zxly 2




Ode Pde Laplace Transforms And Vector Analysis Unit



What Is The Logic Behind Letting F X Y Z X X Y Y Z Z In Pde Separation Of Variables Quora




Ordinary Differential Equations The Decision Of Three Methods Of The Solutions Dx P Dy Q Dz R Mathematics Stack Exchange



2




Partial Differential Equations Formation Of Partial Differential Equations




Ordinary Differential Equations How Is Frac Dx Z X Y Frac Dy Z X Y Frac Dz X 2 Y 2 Equivalent To Frac Y Dx Xdy Zdz 0 Frac Xdx Ydy Zdz 0




If U X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 2 Then Prove That U D 2u Dx 2 D 2u Dy 2 D 2u Sz 2 2




Partial Differentiation If Z X Y X 2 Y 2 Show That әz әx әz әy 2 4 1 әz әx әz әy Youtube



Multivariable Calculus F X Y X Ln Y 2 X Is A Function Of Multiple Variables It S Domain Is A Region In The Xy Plane Ppt Download




Unit Pdf Sine Fourier Series




Solved Find The General Solution Of The Following Partial Chegg Com




Solve The Partial Differential Equation Del Z Del Y Xy




Chapter 1 Maths 3




Solve The Equation X 2p 2 Y 2q 2 Z 2 Mathematics 2 Question Answer Collection



Solved Form Partial Differential Equation By Eliminating The Arbitrary Course Hero



Why Is Separation Of Variables A Valid Method Of Solving Laplace S Equation How Is It Reasonable To Just Assume That V Can Be Expressed As X X Y Y Z Z Quora



How To Eliminate The Arbitrary Function And Hence Obtain The Partial Differential Equation Z X Y F X 2 Y 2 Quora




Math 9 Solutions To Assignment 7 X 2y 1 X 2y I 2 F X Cos Y Z F Y X Z Sin Y Z F Z Xy Z 2 Sin Y Z Pdf Free Download




If Z F X Ay ϕ X Ay Then 2z Y 2 A 2 2z X 2




Solved Questi On L Characterize Each Of The Following Chegg Com



How To Use The Lagrange Method To Solve The Partial Differential Equation Defined By 4 U Sub X Minus 3u Sub Y Equal To Zero With Auxiliary Condition U 0 Y Y 3 Quora



1




Math 467 Partial Differential Equations Exercises Millersville



2
コメント
コメントを投稿